Topology Optimization of Fins for Rapid Heat Storage and Release in Triangular-Inside Tube Units
-
摘要:
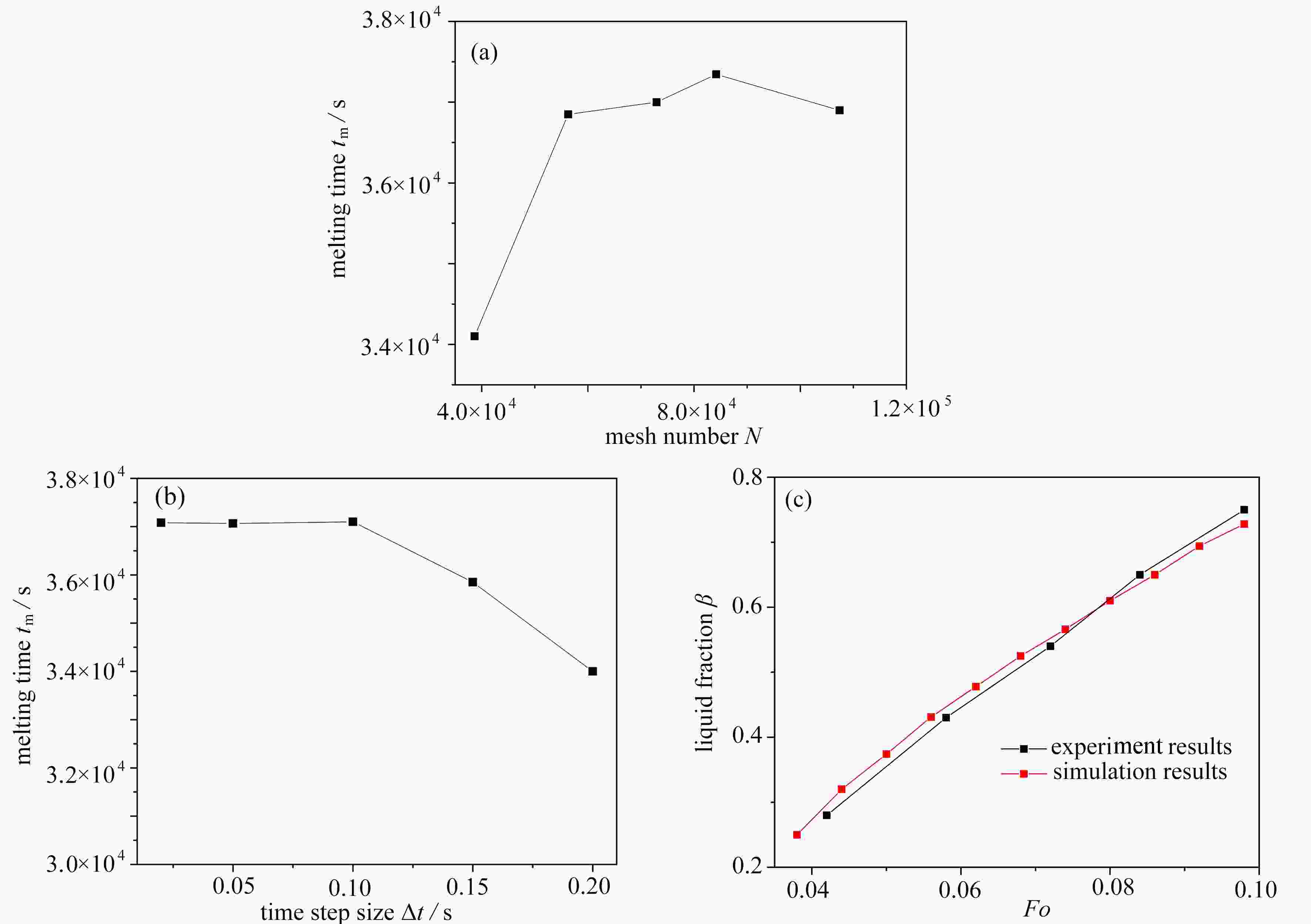
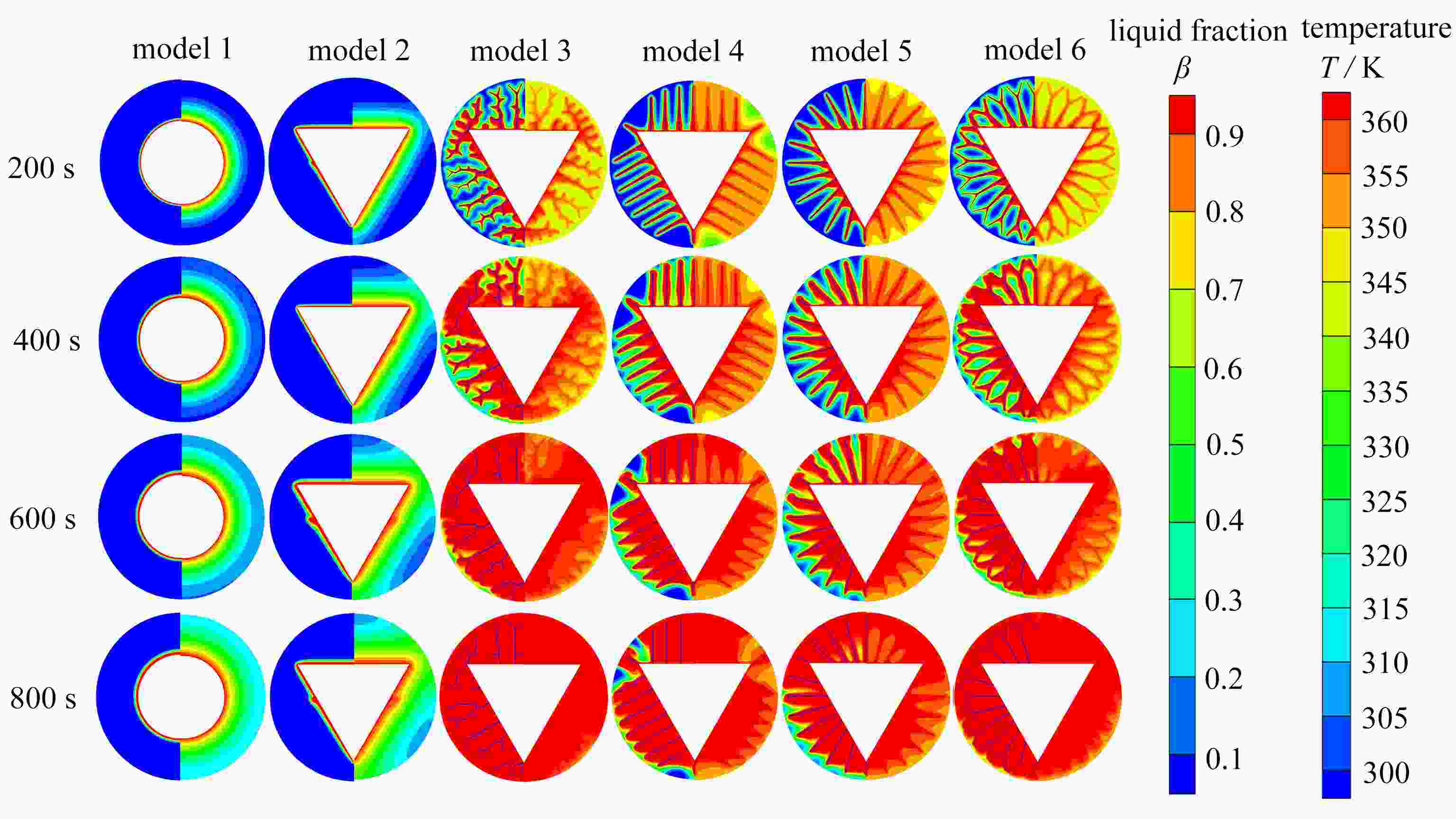
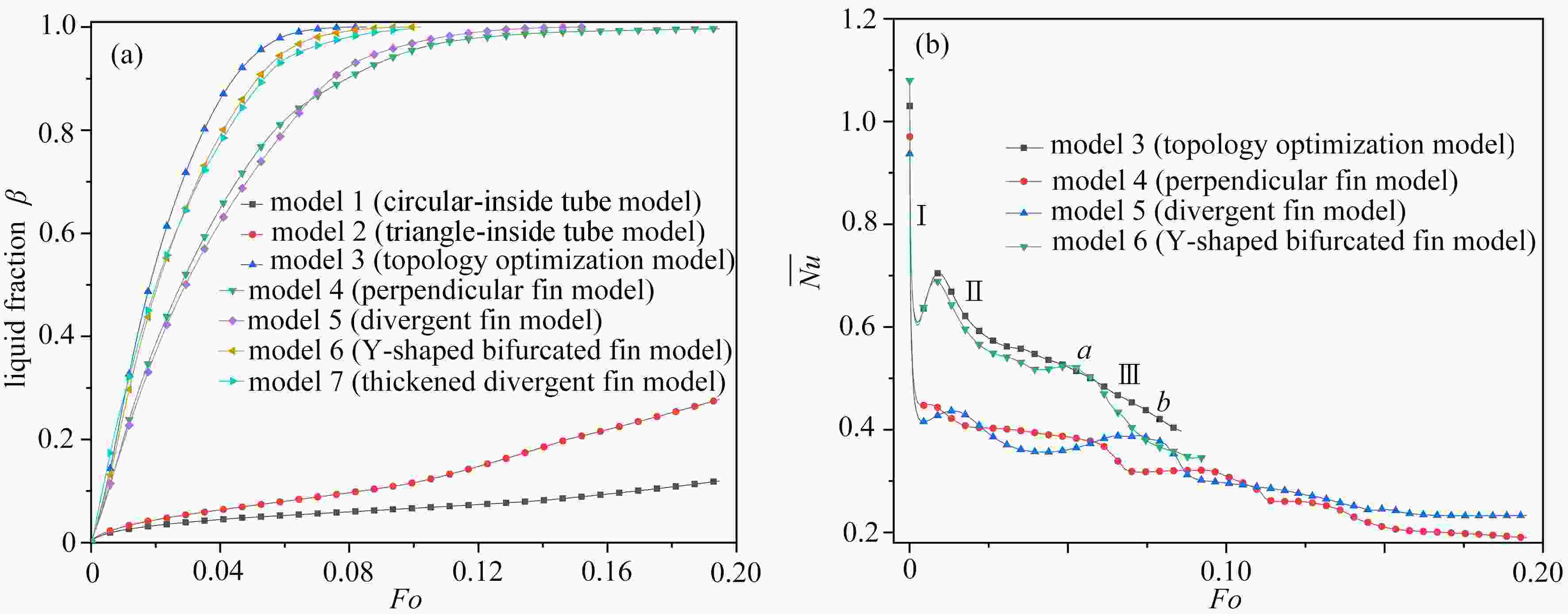
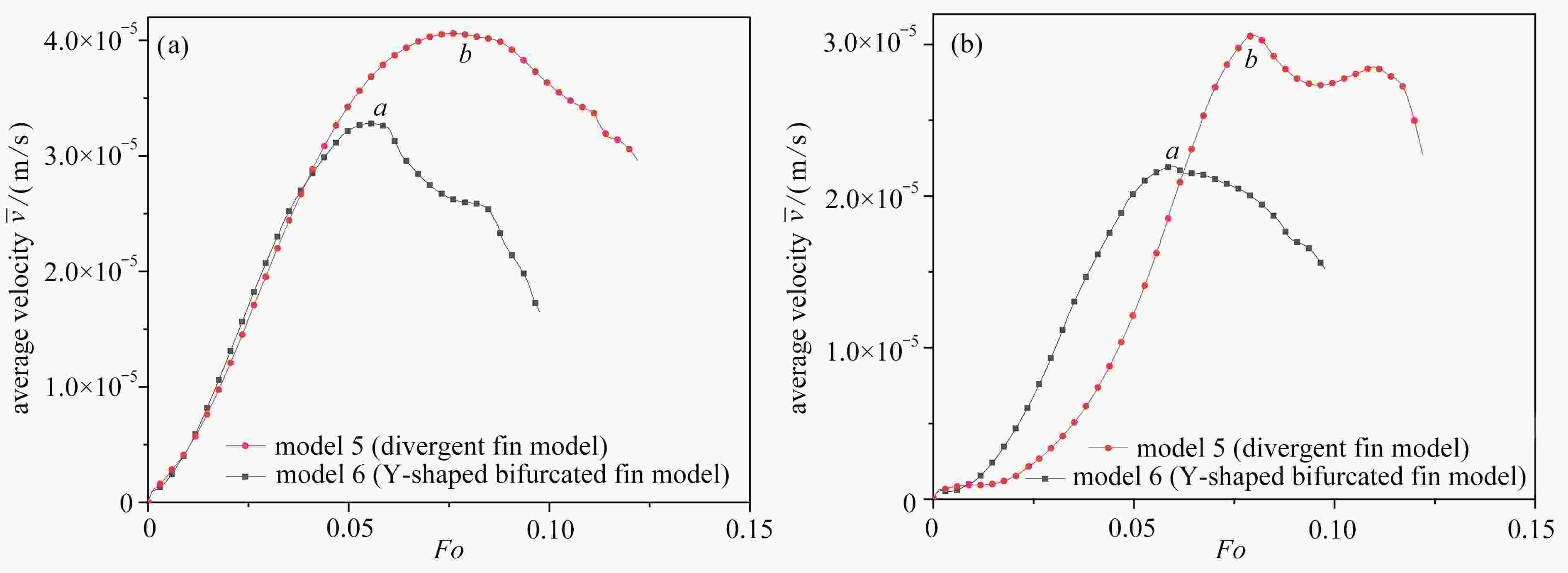
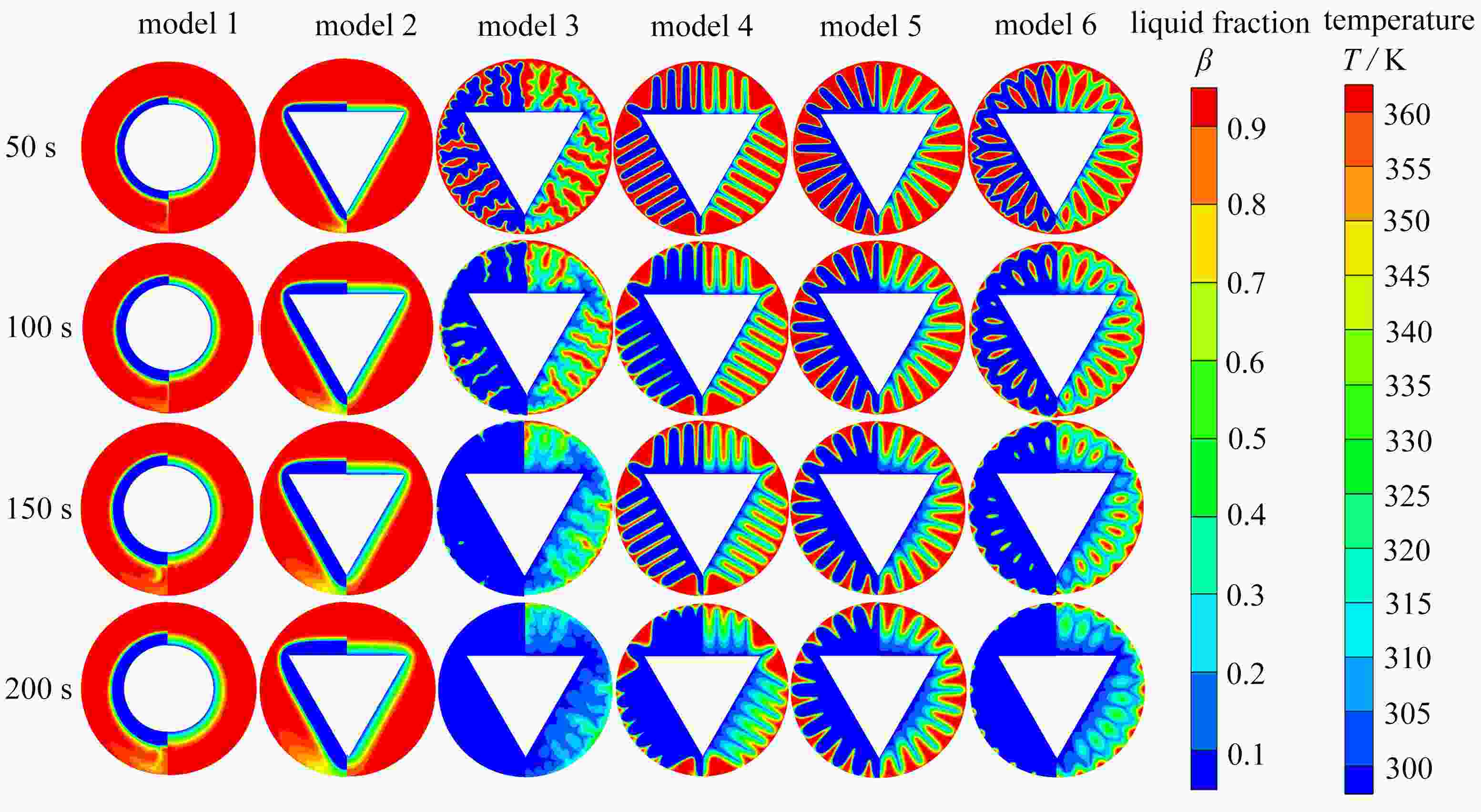
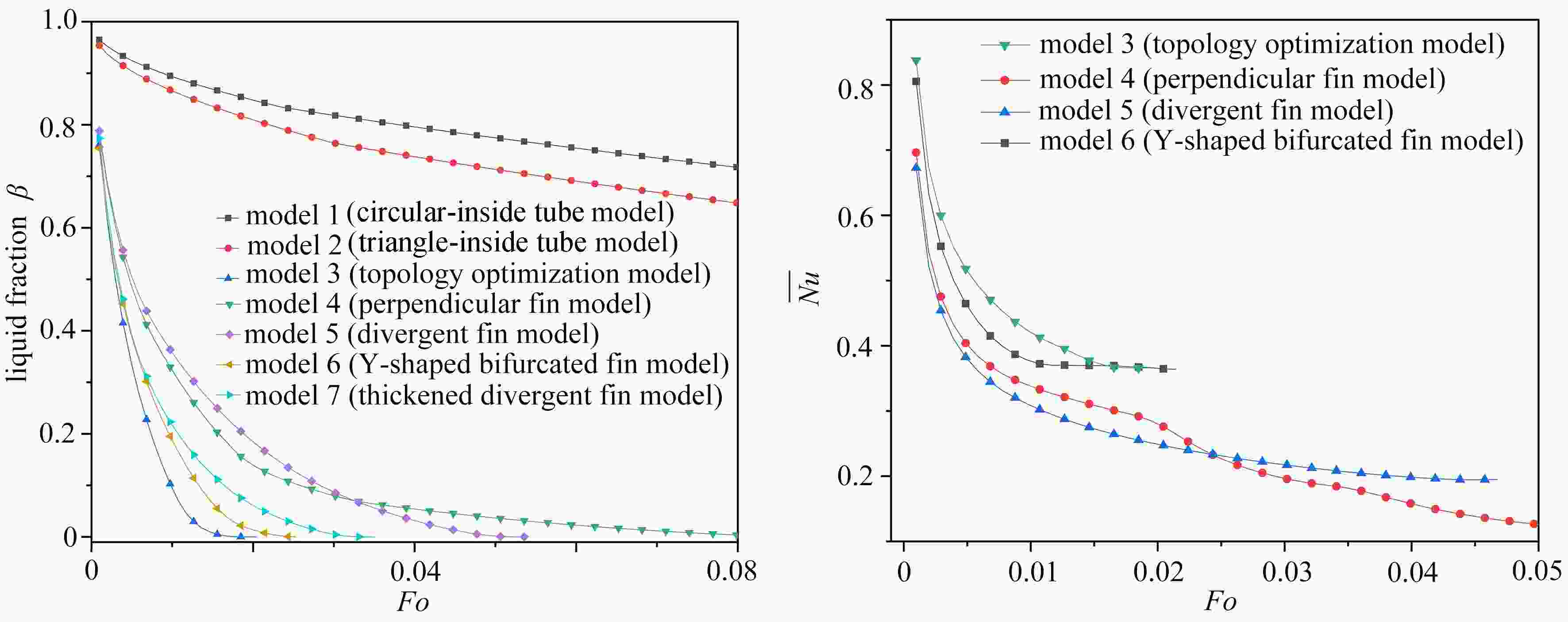
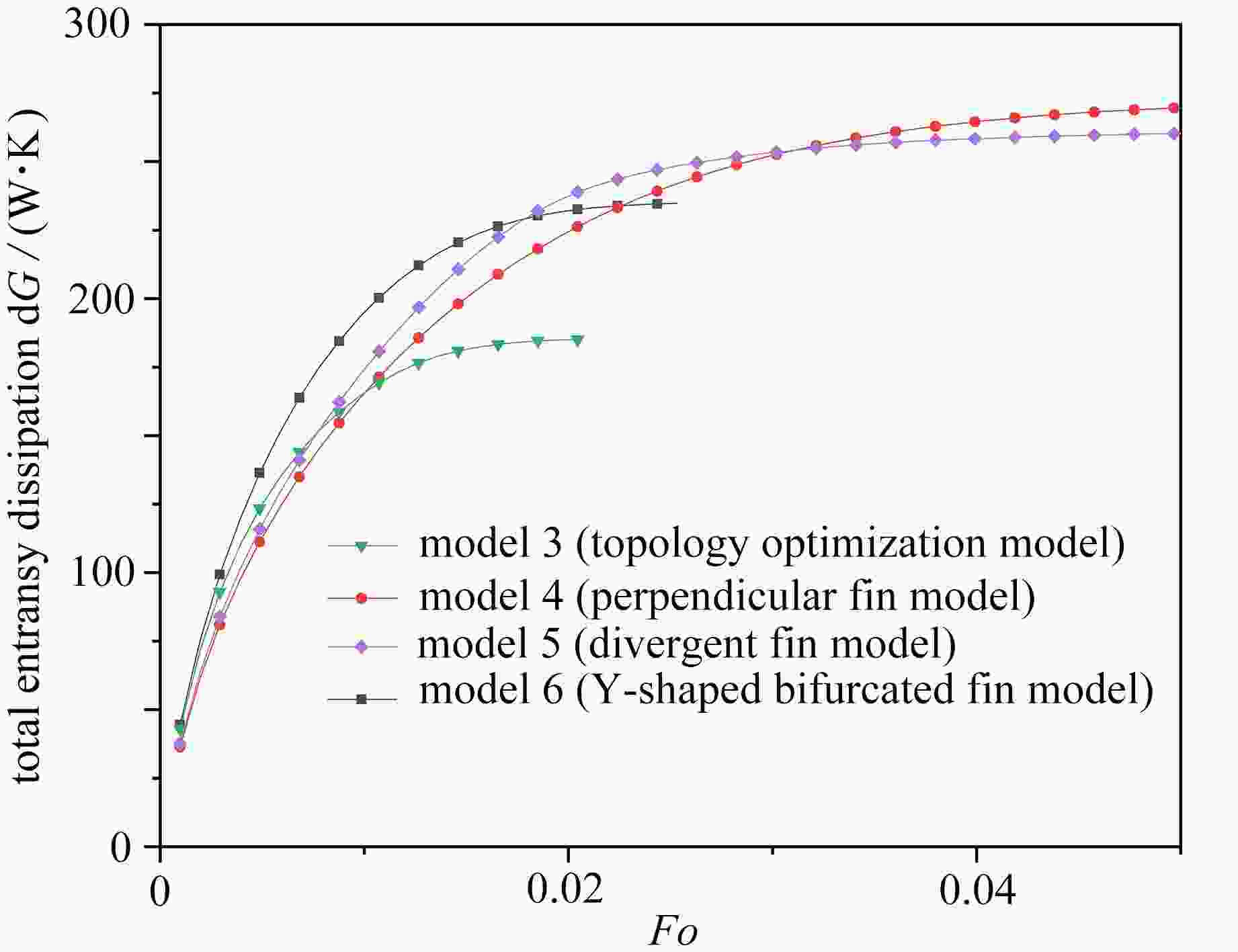
针对传统相变蓄热器传热速率低的问题,提出了一种内三角管式的蓄热器,并基于拓扑优化原理,以强化换热为目的,对其进行肋片设计,重构了拓扑结果,进而提取其拓扑特征重新设计肋片,分析了不同肋片设计对传热能力的影响。结果表明:内三角管式蓄热器相比传统圆管式蓄热器,蓄放热性能大大提高;安装拓扑重构肋片的蓄热器可以使蓄、放热时间缩短,传热效率提高;在蓄热过程中,分叉的拓扑特征可以提高自然对流作用;在放热过程中,安装拓扑重构肋片的蓄热器(火 积)耗散更小,可逆性更好,换热效率更高。
Abstract:A triangular-inside tube accumulator was proposed to solve the problem of low heat transfer rates of traditional phase change accumulators. Based on the topology optimization, the fins were designed for the purpose of enhancing heat transfer, and the topological results were reconstructed, with the topological characteristics extracted to redesign the fin configuration, and the heat transfer capacities of different fin configurations analyzed. The results show that, the triangular-inside tube accumulators have significant advantages of heat storage and release performances over the traditional circular tube accumulators; the accumulators with topologically reconstructed fins can shorten the heat storage and release time and improve the heat transfer efficiency; in the heat storage process, the bifurcated topology characteristics can improve the natural convection; during the heat release process, the accumulators with topologically reconstructed fins are less entransy dissipative, more reversible and more efficient.
-
表 1 物性参数表
Table 1. The physical property parameter table
parameter RT82 Cu solid density ${ { {\rho _{\text{s} } } } / {( { {\text{kg} } \cdot { {\text{m} }^{ { { - 3} } } }} )} }$ 950 8 978 liquid density ${ { {\rho _{\text{l} } } } / {( { {\text{kg} } \cdot { {\text{m} }^{ { { - 3} } } } } )} }$ 770 heat capacity at constant pressure ${{{c_p}} /{( {{\text{J}} \cdot {\text{k}}{{\text{g}}^{{{ - 1}}}} \cdot {{\text{K}}^{{{ - 1}}}}} )}}$ 2 000 381 latent heat ${{{L_{\text{p}}}} / {( {{\text{J}} \cdot {\text{k}}{{\text{g}}^{{{ - 1}}}}} )}}$ 176 000 phase change temperature interval $ {{{T_{{\text{pc}}}}} / {{{\text{K}}^{{{ - 1}}}}}} $ 350.15 ~ 358.15 thermal conductivity ${\lambda /{( {{\text{W}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{{{ - 1}}}} \cdot {{\text{K}}^{{{ - 1}}}}} )}}$ 0.2 387.6 dynamic viscosity ${\mu / {( {{\text{kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{{{ - 1}}}} \cdot {{\text{s}}^{{{ - 1}}}}} )}}$ 0.034 99 thermal expansion coefficient $ {\alpha /{{{\text{K}}^{{{ - 1}}}}}} $ 0.001 表 2 肋片设计参数表
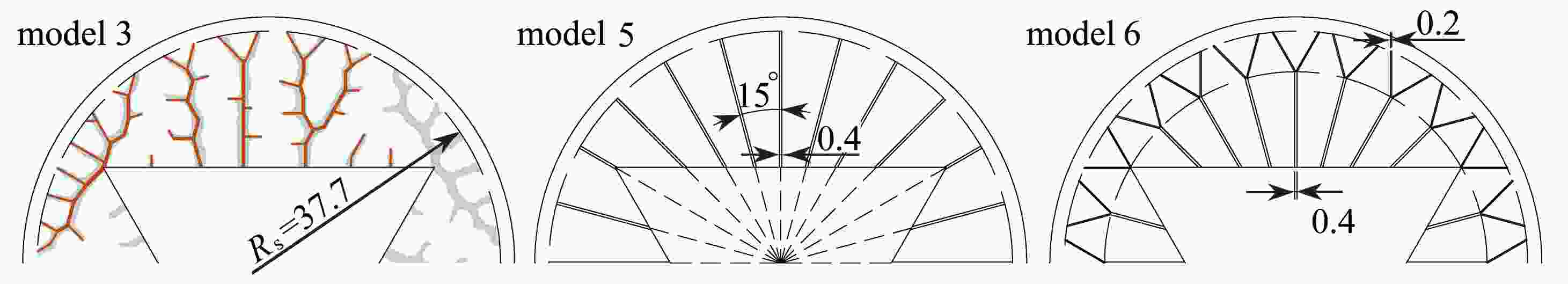
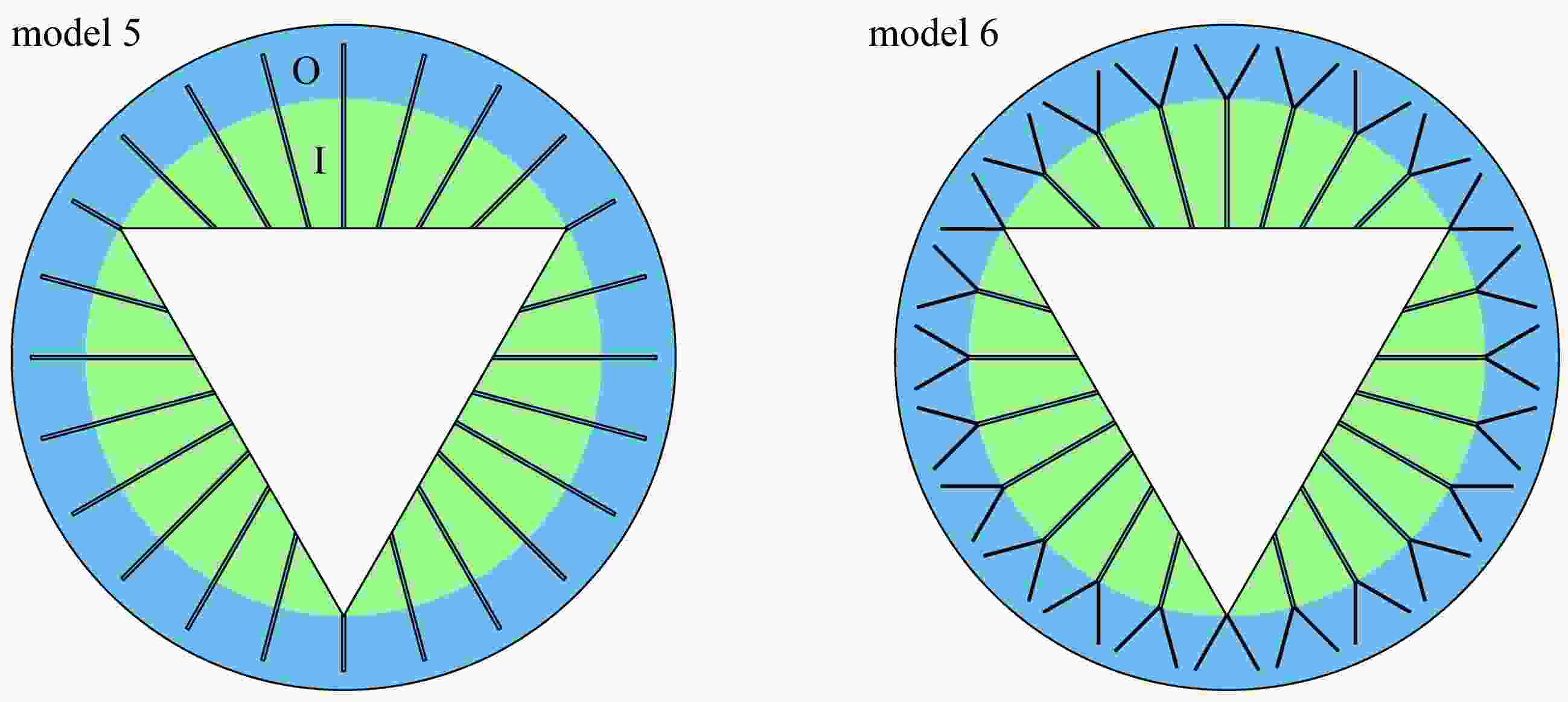
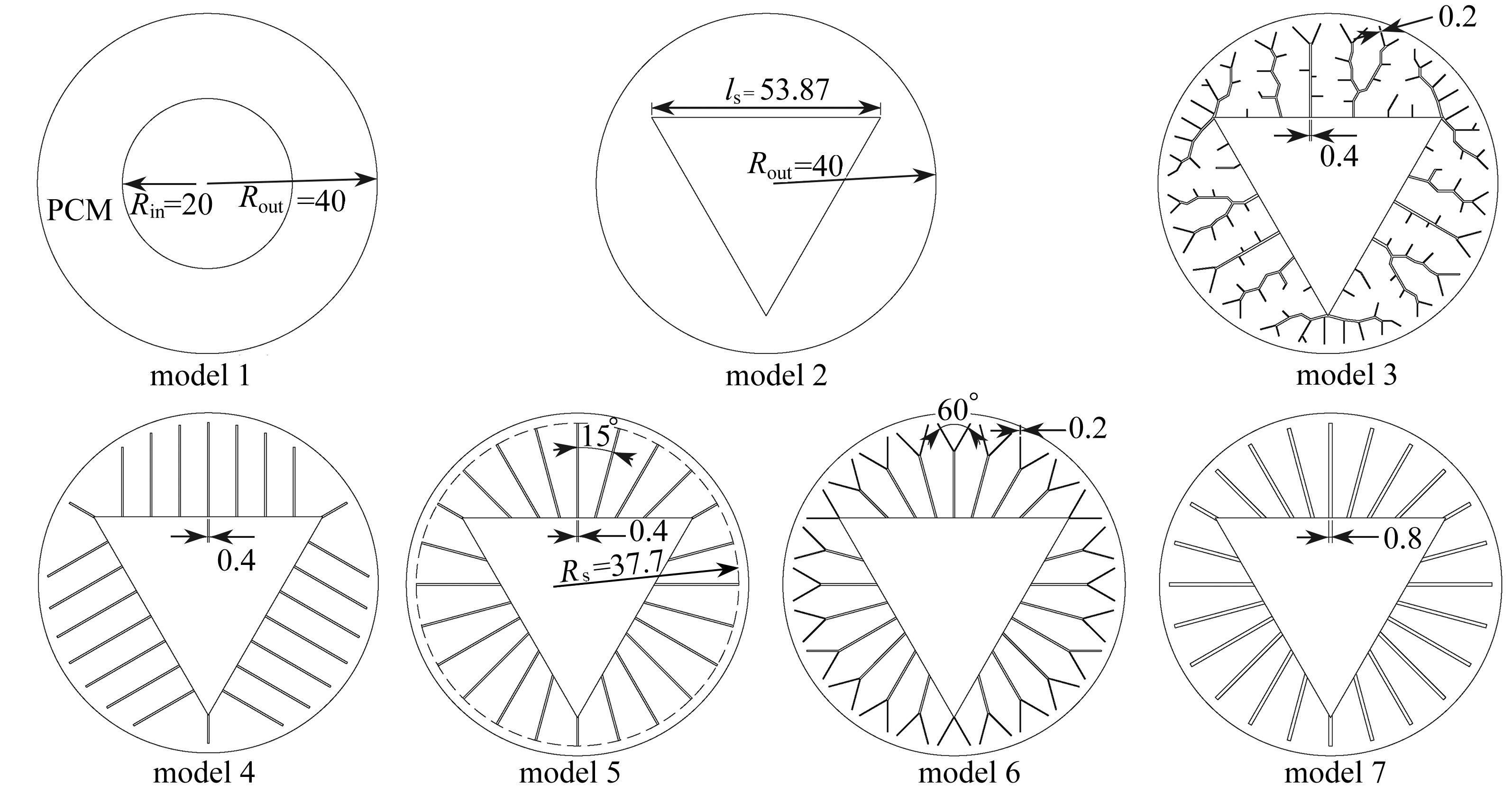
Table 2. The fin design parameter table
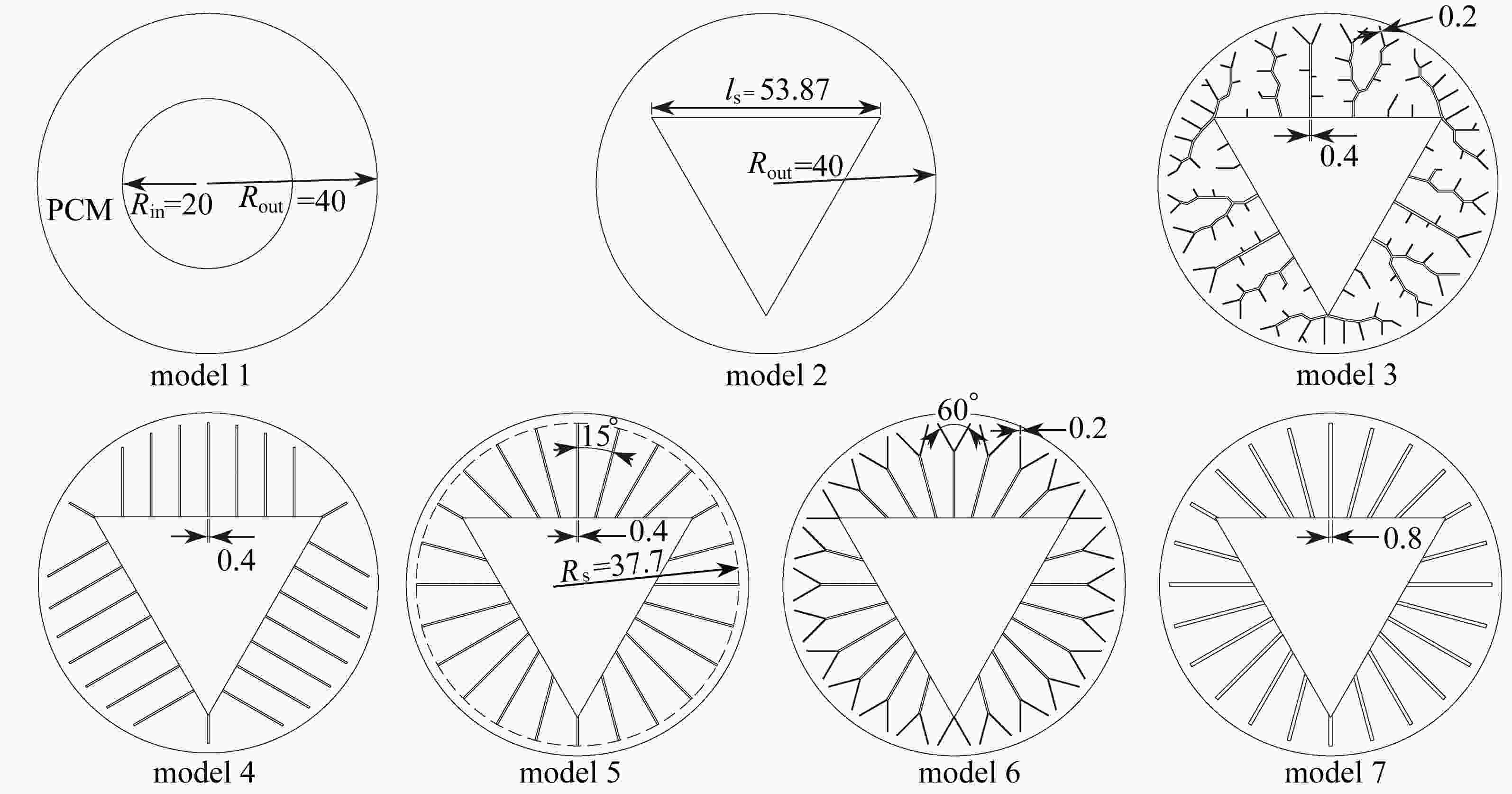
model number number of fins fin thickness d/mm fin proportion η/% model 3 – – 4.72 model 4 24 0.4 4.60 model 5 24 0.4 4.56 model 6 24 – 4.75 model 7 24 0.8 9.12 -
[1] JOUHARA H, KHORDEHGAH N, ALMAHMOUD S, et al. Waste heat recovery technologies and applications[J]. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2018, 6: 268-289. doi: 10.1016/j.tsep.2018.04.017 [2] BISTA S, HOSSEINI S E, OWENS E, et al. Performance improvement and energy consumption reduction in refrigeration systems using phase change material (PCM)[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 142: 723-735. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.07.068 [3] JIN X, SHI D, MEDINA M A, et al. Optimal location of PCM layer in building walls under Nanjing (China) weather conditions[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2017, 129(3): 1767-1778. doi: 10.1007/s10973-017-6307-3 [4] AGYENIM F, HEWITT N, EAMES P, et al. A review of materials, heat transfer and phase change problem formulation for latent heat thermal energy storage systems (LHTESS)[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2010, 14(2): 615-628. [5] ZOU D, MA X, LIU X, et al. Thermal performance enhancement of composite phase change materials (PCM) using graphene and carbon nanotubes as additives for the potential application in lithium-ion power battery[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 120: 33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.12.024 [6] SHEIKHOLESLAMI M, HAQ R, SHAFEE A, et al. Heat transfer simulation of heat storage unit with nanoparticles and fins through a heat exchanger[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 135: 470-478. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.02.003 [7] ZHENG H, WANG C, LIU Q, et al. Thermal performance of copper foam/paraffin composite phase change material[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 157: 372-381. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2017.12.023 [8] PIZZOLATO A, SHARMA A, MAUTE K, et al. Design of effective fins for fast PCM melting and solidification in shell-and-tube latent heat thermal energy storage through topology optimization[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 208: 210-227. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.10.050 [9] ISMAIL K A R, ALVES C L F, MODESTO M S. Numerical and experimental study on the solidification of PCM around a vertical axially finned isothermal cylinder[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2001, 21(1): 53-77. doi: 10.1016/S1359-4311(00)00002-8 [10] SCIACOVELLI A, GAGLIARDI F, VERDA V. Maximization of performance of a PCM latent heat storage system with innovative fins[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 137: 707-715. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.07.015 [11] 夏天翔, 姚卫星. 连续体结构拓扑优化方法评述[J]. 航空工程进展, 2011, 2(1): 1-11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8190.2011.01.001XIA Tianxiang, YAO Weixing. A survey of topology optimization of continuum structure[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2011, 2(1): 1-11.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8190.2011.01.001 [12] HAN X, LIU H, XIE G, et al. Topology optimization for spider web heat sinks for electronic cooling[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 195: 117154. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117154 [13] TIAN Y, LIU X, XU Q, et al. Bionic topology optimization of fins for rapid latent heat thermal energy storage[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 194: 117104. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117104 [14] 游吟, 赵耀, 赵长颖, 等. 相变储热单元内肋片结构的拓扑优化[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(11): 1191-1199 doi: 10.1360/N972018-01134YOU Yin, ZHAO Yao, ZHAO Changying, et al. The topology optimization of the fin structure in latent heat storage[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(11): 1191-1199.(in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/N972018-01134 [15] 郑宇豪, 赵明. 整体旋转式三角形管相变蓄热器性能及场协同分析[J]. 建模与仿真, 2021, 10(2): 292-304 doi: 10.12677/MOS.2021.102030ZHENG Yuhao, ZHAO Ming. Performance and field synergy analysis of integral rotating phase change heat accumulator with triangular tube[J]. Modeling and Simulation, 2021, 10(2): 292-304.(in Chinese) doi: 10.12677/MOS.2021.102030 [16] YUAN Y, CAO X, XIANG B, et al. Effect of installation angle of fins on melting characteristics of annular unit for latent heat thermal energy storage[J]. Solar Energy, 2016, 136: 365-378. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.07.014 [17] TCHERNIAK D. Topology optimization of resonating structures using SIMP method[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2002, 54(11): 1605-1622. doi: 10.1002/nme.484 [18] 孙国民, 张效忠, 孙延华. 基于特征值分析的多尺度结构优化设计方法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(6): 630-640SUN Guomin, ZHANG Xiaozhong, SUN Yanhua. Multi-scale structure optimization design based on eigenvalue analysis[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(6): 630-640.(in Chinese) [19] SVANBERG K. The method of moving asymptotes: a new method for structural optimization[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1987, 24(2): 359-373. doi: 10.1002/nme.1620240207 [20] KAMKARI B, SHOKOUHMAND H. Experimental investigation of phase change material melting in rectangular enclosures with horizontal partial fins[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 78: 839-851. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.07.056 [21] GUO Z Y, ZHU H Y, LIANG X G. Entransy: a physical quantity describing heat transfer ability[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2007, 50(13/14): 2545-2556. [22] 韩光泽, 过增元. 导热能力损耗的机理及其数学表述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27(17): 98-102 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2007.17.019HAN Guangze, GUO Zengyuan. Physical mechanism of heat conduction ability dissipation and its analytical expression[J]. Proceedings of the Chinese Society of Electrical Engineering, 2007, 27(17): 98-102.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-8013.2007.17.019 -




 下载:
下载:





 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号