Linear Bending Analysis of Functionally Graded Sandwich Shells With the Meshless Method Based on the Layer-Wise Theory
-
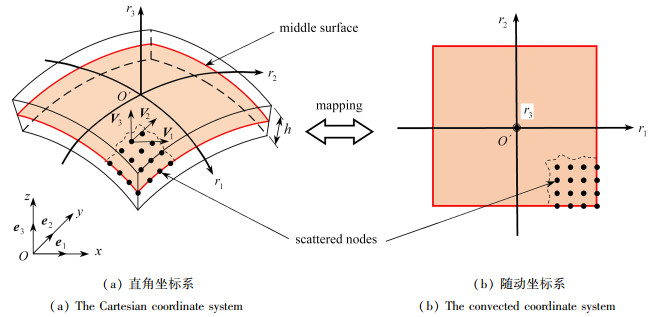
摘要: 基于3D连续壳理论和一阶剪切变形理论,采用分层法,提出了一种求解功能梯度三明治壳线性弯曲问题的移动最小二乘无网格法. 通过映射技术,将随动坐标系上的二维无网格节点信息映射到三维壳中,并在随动坐标系上形成移动最小二乘近似的形函数. 因基于3D连续壳理论的壳数值解答无法像特定壳一样给出其厚度方向的显式表达式,该文将功能梯度三明治材料壳结构中材料参数变化的部分划分成若干层,得到每层的材料参数为常数. 利用最小势能原理,推导出了功能梯度三明治壳线性弯曲的无网格控制方程. 通过引入一个厚度方向的线性变换,使得每层厚度方向的Gauss积分均在-1至1区间内,不违背一阶剪切变形理论. 采用完全转化法施加本质边界条件. 以功能梯度三明治板、柱壳、双曲扁壳经典几何形状壳为例,讨论了不同梯度系数、径厚比和曲率半径等对数值结果的影响,并将计算结果与文献解对比. 研究表明,该方法在求解不同形状的功能梯度三明治壳线性弯曲问题时,具有收敛性好、计算精度高的特点.Abstract: Based on the 3D continuous shell theory and the 1st-order shear deformation theory, a moving least squares meshless method was proposed for solving the linear bending problem of functionally graded sandwich shells with the layered method. With the mapping technology, the 2D meshless node information on the convected coordinate system was mapped on the 3D shell, and the shape function of moving least squares (MLS) approximation was formed on the convected coordinate system. Due to the inability of shell numerical solutions based on the 3D continuous shell theory to provide an explicit expression for the thickness direction of a specific shell, the portion of material parameter changes in the functionally graded sandwich material shell structure was divided into several layers, and the material parameters of each layer were obtained as constants. The governing meshless equation for linear bending of functionally graded sandwich shells was derived under the principle of minimum potential energy. Through introduction of a linear transformation in the thickness direction, the Gaussian integral in the thickness direction of each layer was bounded within the range of -1 to 1, without violation of the 1st-order shear deformation theory (FSDT). The essential boundary conditions were employed with the complete transformation method. Finally, the effects of different gradient coefficients, diameter to thickness ratios, and curvature radii on numerical results were discussed through examples of functionally graded sandwich plates, cylindrical shells, and hyperbolic shallow shells with classical geometric shapes. The calculated results were compared with the literature solutions. The results show that, the proposed method has the characteristics of good convergence and high computation accuracy in solving linear bending problems of functional graded sandwich shells with different shapes.
-
表 1 功能梯度材料组成元素
Table 1. Properties of the FGM components
property Al ceramic Al2O3 ZrO2 E/GPa 70 380 200 ν 0.3 0.3 0.3 表 2 分层数及节点数对铝/氧化铝方板中点归一化挠度w1的影响(p=10,Type B)
Table 2. Effects of the numbers of layers and nodes on central deflectionw1 of the Al/Al2O3 square plate (p=10, Type B)
layers present 5×5 9×9 13×13 1/4/1 0.829 7 0.826 1 0.826 1 1/8/1 0.864 8 0.861 0 0.861 0 1/12/1 0.861 9 0.858 0 0.858 0 1/16/1 0.860 8 0.857 0 0.857 0 表 3 不同梯度指数p下,铝/氧化铝方板中点归一化挠度w1(Type B)
Table 3. Normalized central deflection w1 for the Al/Al2O3 square plate with different gradient indices p(Type B)
表 4 不同层状厚度与不同梯度指数p下,铝/氧化锆方板中点归一化挠度w2 (Type C)
Table 4. Normalized central deflection w2 for the Al/ZrO2 square plate with different layer thicknesses and gradient indices p(Type C)
p theory 1-0-1 2-1-2 1-1-1 2-2-1 1-2-1 1 Nguyen et al. [35](ITSDT) 0.323 5 0.306 2 0.291 9 0.280 8 0.270 9 Zenkour[36](FSDT) 0.324 8 0.307 5 0.293 0 0.281 7 0.271 7 Neves et al. [34](quasi-3D) - 0.307 0 0.292 9 0.282 0 0.272 2 present 0.324 3 0.307 1 0.292 7 0.281 4 0.271 5 5 Nguyen et al. [35](ITSDT) 0.409 1 0.391 7 0.371 3 0.349 5 0.334 7 Zenkour[36](FSDT) 0.411 2 0.394 2 0.373 6 0.351 2 0.336 3 Neves et al. [34](quasi-3D) - 0.390 5 0.370 5 0.349 0 0.334 7 present 0.410 8 0.393 7 0.372 2 0.350 9 0.336 0 10 Nguyen et al. [35](ITSDT) 0.417 5 0.403 9 0.385 4 0.362 0 0.348 2 Zenkour[36](FSDT) 0.419 2 0.406 6 0.387 9 0.364 0 0.350 0 Neves et al. [34](quasi-3D) - 0.402 6 0.384 3 0.361 2 0.348 0 present 0.418 9 0.406 2 0.387 5 0.363 6 0.349 7 表 5 分层数及节点数对四边简支铝/氧化锆柱壳中点挠度w3的影响(p=1,Type A)
Table 5. Effects of the numbers of layers and nodes on central deflection w3 of the simply supported Al/ZrO2 cylindrical shell (p=1, Type A)
number of layers present 5×5 9×9 13×13 17×17 4 0.060 76 0.060 07 0.060 10 0.060 12 8 0.060 97 0.060 29 0.060 30 0.060 34 12 0.061 01 0.060 33 0.060 36 0.060 38 表 6 不同边界条件与不同梯度指数p下,铝/氧化锆柱壳中点归一化挠度w3(Type A)
Table 6. Normalized central deflection w3 for the Al/ZrO2 cylindrical shell with different boundary conditions and gradient indices p(Type A)
表 7 不同径厚比R/h与不同梯度指数p下,四边简支铝/氧化锆柱壳中点归一化挠度w3(Type A)
Table 7. Normalized central deflection w3 for the simply supported Al/ZrO2 cylindrical shell with different radius-to-thickness ratios R/h and gradient indices p(Type A)
p R/h method FSDT[37] CST[37] analytical[38] kp-Ritz[24] present 1 50 0.004 24 0.004 08 0.004 30 0.004 28 0.004 25 100 0.060 56 0.060 02 0.060 91 0.060 72 0.060 30 200 0.725 84 0.724 70 0.727 10 0.728 30 0.722 21 2 50 0.004 64 0.004 46 0.004 70 0.004 69 0.004 67 100 0.066 40 0.065 78 0.066 79 0.066 78 0.066 37 200 0.803 07 0.801 73 0.805 60 0.805 70 0.801 18 表 8 分层数及节点数对四边简支Type B铝/氧化铝柱壳中点挠度wc×10-11的影响,p=1,R/h=1 000(单位: m)
Table 8. Effects of the numbers of layers and nodes on central deflection wc×10-11 for the simply supported Al/Al2O3 cylindrical shell, p=1, R/h=1 000, Type B (unit: m)
layers present 31×3 51×5 71×7 91×9 1/4/1 3 946.5 4 155.7 4 172.5 4 173.7 1/8/1 3 950.7 4 159.2 4 176.2 4 177.1 1/12/1 3 951.5 4 159.9 4 176.9 4 177.3 表 9 不同径厚比R/h与不同梯度指数p下,四边简支Type B铝/氧化铝柱壳中点挠度wc×10-11(单位: m)
Table 9. Normalized central deflection wc×10-11 for the simply supported Al/Al2O3 cylindrical shell with different radius-to-thickness ratios R/h and gradient indices p, Type B (unit: m)
表 10 分层数及节点数对四边简支铝/氧化铝柱壳中点挠度w4的影响
Table 10. Effects of the numbers of layers and nodes on central deflection w4 of the simply supported Al/Al2O3 cylindrical shell
layers present 5×5 9×9 13×13 17×17 4 8.873 9 8.762 6 8.759 9 8.760 0 8 9.010 0 8.897 0 8.894 3 8.894 4 12 9.036 3 8.923 0 8.920 2 8.920 4 16 9.045 6 8.932 1 8.929 4 8.929 5 表 11 不同梯度指数p下,四边简支铝/氧化铝不同形状壳中点归一化挠度w4
Table 11. Normalized central deflectionw4 for the simply supported Al/Al2O3 different shells with various gradient indices p
shell type method p 0 1 5 10 ∞ cylindrical shell (Rx/a=5, Ry/b=∞) ESDT[37] 4.526 5 8.964 8 13.942 0 15.460 0 24.572 0 FSDT[37] 4.492 1 8.907 2 13.683 0 15.152 0 24.385 0 present 4.525 5 8.920 2 13.827 4 15.401 0 24.567 1 spherical shell (Rx/a=5, Ry/b=5) ESDT[37] 4.157 1 8.119 3 12.816 0 14.333 0 22.567 0 FSDT[37] 4.128 5 8.072 9 12.601 0 14.071 0 22.412 0 present 4.161 1 8.073 9 12.699 3 14.268 6 22.588 9 hyperbolic paraboloid shell (Rx/a=5, Ry/b=-5) ESDT[37] 4.664 6 9.286 8 14.362 0 15.876 0 25.322 0 FSDT[37] 4.627 8 9.224 6 14.086 0 15.550 0 25.122 0 present 4.653 9 9.239 8 14.250 7 15.815 4 25.263 9 elliptical paraboloid shell (Rx/a=5, Ry/b=7.5) ESDT[37] 4.300 3 8.444 2 13.253 0 14.772 0 23.344 0 FSDT[37] 4.269 4 8.393 7 13.021 0 14.493 0 23.177 0 present 4.303 0 8.399 1 13.136 1 14.709 9 23.359 2 -
[1] KOIZUMI M. The concept of FGM[J]. Ceramic Transactions, 1993, 34: 3-10. [2] 沈惠申. 功能梯度复合材料板壳结构的弯曲、屈曲和振动[J]. 力学进展, 2004, 34(1): 53-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2004.01.006SHEN Huishen. Bending, buckling and vibration of functionally graded plates and shells[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2004, 34(1): 53-60. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2004.01.006 [3] LIEW K M, ZHAO X, FERREIRA A J M. A review of meshless methods for laminated and functionally graded plates and shells[J]. Composite Structures, 2011, 93(8): 2031-2041. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.02.018 [4] 李尧臣, 亓峰, 仲政. 功能梯度矩形板的近似理论与解析解[J]. 力学学报, 2010, 42(4): 670-681. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB201004013.htmLI Yaochen, QI Feng, ZHONG Zheng. Approximation theory and analytical solution for functionally graded piezoelectric rectangular plates[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2010, 42(4): 670-681. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB201004013.htm [5] WOODWARD B, KASHTALYAN M. Three-dimensional elasticity solution for bending of transversely isotropic functionally graded plates[J]. European Journal of Mechanics A: Solids, 2011, 30(5): 705-718. doi: 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2011.04.003 [6] 沈璐璐, 蔡方圆, 杨博. 功能梯度压电板柱面弯曲的弹性力学解[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2023, 44(3): 272-281. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430224SHEN Lulu, CAI Fangyuan, YANG Bo. Elastic solutions for cylindrical bending of functionally graded piezoelectric material plates[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2023, 44(3): 272-281. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430224 [7] 张靖华, 李世荣, 马连生. 功能梯度截顶圆锥壳的热弹性弯曲精确解[J]. 力学学报, 2008, 40(2): 185-193. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2008.02.006ZHANG Jinghua, LI Shirong, MA Liansheng. Exact solution of thermoelastic bending for functionally graded truncated conical shells[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2008, 40(2): 185-193. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2008.02.006 [8] PAYETTE G S, REDDY J N. A seven-parameter spectral/hp finite element formulation for isotropic, laminated composite and functionally graded shell structures[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 278: 664-704. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2014.06.021 [9] PARAND A A, ALIBEIGLOO A. Static and vibration analysis of sandwich cylindrical shell with functionally graded core and viscoelastic interface using DQM[J]. Composites(Part B): Engineering, 2017, 126: 1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.05.071 [10] 刘涛, 李朝东, 汪超, 等. 基于三阶剪切变形理论的压电功能梯度板静力学等几何分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(1): 73-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ202101012.htmLIU Tao, LI Chaodong, WANG Chao, et al. Static iso-geometric analysis of piezoelectric functionally graded plate based on third-order shear deformation theory[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(1): 73-85. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ202101012.htm [11] 黄干云, 汪越胜, 余寿文. 功能梯度材料的平面断裂力学分析[J]. 力学学报, 2005, 37(1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB200501001.htmHUANG Ganyun, WANG Yuesheng, YU Shouwen. A new multi-layered model for in-plane fracture analysis of functionally graded materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2005, 37(1): 1-8. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXXB200501001.htm [12] WANG Y S, HUANG G Y, GROSS D. On the mechanical modeling of functionally graded interfacial zone with a Griffith crack: anti-plane deformation[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2003, 125(3): 189-205. [13] 黄立新, 姚祺, 张晓磊, 等. 基于分层法的功能梯度材料有限元分析[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2013(2): 43-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2013.02.009HUANG Lixin, YAO Qi, ZHANG Xiaolei, et al. Finite element analysis of functionally graded materials based on layering method[J]. Composite Science and Engineering, 2013(2): 43-48. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2013.02.009 [14] NIKBAKHT S, SALAMI S J, SHAKERI M. Three dimensional analysis of functionally graded plates up to yielding, using full layer-wise finite element method[J]. Composite Structures, 2017, 182: 99-115. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.09.022 [15] BRISCHETTO S. A 3D layer-wise model for the correct imposition of transverse shear/normal load conditions in FGM shells[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2018, 136: 50-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.12.013 [16] 龙述尧, 刘凯远, 李光耀. 功能梯度材料中的无网格局部径向点插值法[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 34(3): 41-44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2472.2007.03.010LONG Shuyao, LIU Kaiyuan, LI Guangyao. A meshless local radial point interpolation method for the analysis of functionally graded materials[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2007, 34(3): 41-44. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2472.2007.03.010 [17] 邵玉龙, 段庆林, 李锡夔, 等. 功能梯度材料的二阶一致无网格法[J]. 工程力学, 2017, 34(3): 15-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201703002.htmSHAO Yulong, DUAN Qinlin, LI Xikui, et al. Quadratically consistent meshfree method for functionally graded materials[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34(3): 15-21. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX201703002.htm [18] QIAN L F, BATRA R C, CHEN L M. Static and dynamic deformations of thick functionally graded elastic plates by using higher-order shear and normal deformable plate theory and meshless local Petrov-Galerkin method[J]. Composites(Part B): Engineering, 2004, 35: 685-697. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2004.02.004 [19] LEE Y Y, ZHAO X, LIEW K M. Thermoelastic analysis of functionally graded plates using the element-free kp-Ritz method[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2009, 18(3): 035007. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/18/3/035007 [20] THAI C H, DO V N V, NGUYEN-XUAN H. An improved moving Kriging-based meshfree method for static, dynamic and buckling analyses of functionally graded isotropic and sandwich plates[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2016, 64: 122-136. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2015.12.003 [21] HOSSEINI S, RAHIMI G, ANANI Y. A meshless collocation method based on radial basis functions for free and forced vibration analysis of functionally graded plates using FSDT[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2021, 125: 168-177. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2020.12.016 [22] VU T V, KHOSRAVIFARD A, HEMATIYAN M R, et al. Enhanced meshfree method with new correlation functions for functionally graded plates using a refined inverse sin shear deformation plate theory[J]. European Journal of Mechanics A: Solids, 2019, 74: 160-175. doi: 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2018.11.005 [23] SLADEK J, SLADEK V, ZHANG C, et al. Static and dynamic analysis of shallow shells with functionally graded and orthotropic material properties[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2008, 15(2): 142-156. doi: 10.1080/15376490701810480 [24] ZHAO X, LEE Y Y, LIEW K M. Thermoelastic and vibration analysis of functionally graded cylindrical shells[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2009, 51(9/10): 694-707. [25] ZHAO X, LIEW K M. A mesh-free method for analysis of the thermal and mechanical buckling of functionally graded cylindrical shell panels[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2010, 45: 297-310. doi: 10.1007/s00466-009-0446-8 [26] ZHAO X, LIEW K M. Free vibration analysis of functionally graded conical shell panels by a meshless method[J]. Composite Structures, 2011, 93(2): 649-664. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2010.08.014 [27] MELLOULI H, JRAD H, WALI M, et al. Meshfree implementation of the double director shell model for FGM shell structures analysis[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2019, 99: 111-121. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2018.10.013 [28] SIMO J C, FOX D D, RIFAI M S. Formulation and computational aspects of a stress resultant geometrically exact shell model[J]. Computation Mechanics, 1990, 55: 751-759. [29] WANG L, LIU Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Static and dynamic analysis of thin functionally graded shell with in-plane material inhomogeneity[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2021, 193: 106165. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.106165 [30] AHMAD S, IRONS B M, ZIENKIEWICZ O C. Analysis of thick and thin shell structures by curved finite elements[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1970, 2: 419-451. doi: 10.1002/nme.1620020310 [31] SALKAUSKAS P L. Surfaces generated by moving least squares methods[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1981, 37(155): 141-158. doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1981-0616367-1 [32] CHEN J S, PAN C, WU C T, et al. Reproducing kernel particle methods for large deformation analysis of non-linear structures[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1996, 139(4): 195-227. [33] TIMOSHENKO S. Theory of Plates and Shells[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1959. [34] NEVES A M A, FERREIRA A J M, CARRERA E, et al. Static, free vibration and buckling analysis of isotropic and sandwich functionally graded plates using a quasi-3D higher-order shear deformation theory and a meshless technique[J]. Composites(Part B): Engineering, 2013, 44(1): 657-674. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.01.089 [35] NGUYEN V H, NGUYEN T K, THAI H T, et al. A new inverse trigonometric shear deformation theory for isotropic and functionally graded sandwich plates[J]. Composites(Part B): Engineering, 2014, 66: 233-246. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.05.012 [36] ZENKOUR A M. A comprehensive analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates, part 1: deflection and stresses[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2005, 42(18): 5224-5242. [37] SAYYAD A S, GHUGAL Y M. Static and free vibration analysis of doubly-curved functionally graded material shells[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 269: 114045. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114045 [38] HUAN D T, TU T M, QUOC T H. Analytical solutions for bending, buckling and vibration analysis of functionally graded cylindrical panel[J]. Vietnam Journal of Science Technology, 2017, 55(5): 587-597. doi: 10.15625/2525-2518/55/5/8843 [39] CARRERA E, BRISCHETTO S, CINEFRA M, et al. Effects of thickness stretching in functionally graded plates and shells[J]. Composites(Part B): Engineering, 2011, 42(2): 123-133. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2010.10.005 -





 下载:
下载:








 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号