Research on Bridge Performance Degradation Prediction Based on Combination of the D-S Theory and the Markov Chain
-
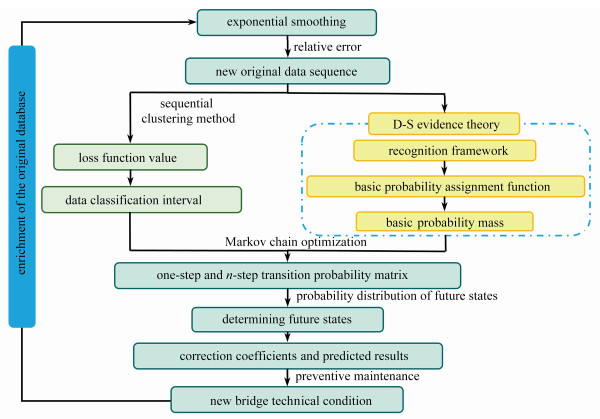
摘要: 为准确预测桥梁性能退化,考虑到数据随机性和微小扰动发生状态跳跃,提出了一种D-S(Dempster-Shafer)证据理论和Markov链组合的桥梁性能退化组合预测模型和性能退化率的概念.该模型基于指数平滑(exponential smoothing, ES)方法获得新的预测数据序列,并利用Markov链和D-S理论不断进行优化,从而实现桥梁性能退化的组合预测.实际工程的应用结果表明:性能退化率可以直观地表征在梁性能退化的速度.其次,该模型的平均相对误差为1.54%,较于回归、灰色和模糊加权Markov链模型,精度分别提高了1.11%,0.88%和2.8%,而后验差比值为0.242,小于0.35;模型的标准差为9.021,相比其他模型分别减小了3.978,3.405和7.500,而变异系数为0.109,均小于其他模型,验证了组合预测模型在精度和稳定性方面的优越性,可为在役桥梁结构性能退化预测与维护提供理论基础.Abstract: To accurately predict bridge performance degradation, the inherent data randomness and the subtle perturbations leading to state transitions were considered. A combined prediction method for the bridge performance degradation based on the D-S theory and the Markov chain, and the performance degradation rate concept, were proposed. In this model, the exponential smoothing (ES) methodology was employed as the basis for generating new sequences of predictive data. It was continuously optimized through the utilization of the Markov chains and the Dempster-Shafer (D-S) evidence theory. The combined prediction of bridge performance degradation was achieved. The application results from practical engineering show that, the performance degradation rate serves as an intuitive indicator of the speed at which the bridge performance degrades. Subsequently, the combined model demonstrates an average relative error of 1.54%, improves by 1.11%, 0.88%, and 2.8% in accuracy, respectively in comparison with other models of the regression, the grey system, and the fuzzy weighted Markov chain. Additionally, the calculated posterior difference ratio is 0.242, well below the established threshold of 0.35. In terms of stability, the standard deviation of the model is 9.021, reduces by 3.978, 3.405 and 7.500, respectively compared with those of the other 3 models. The coefficient of variation is 0.109, indicating a significant reduction in comparison to those of the other models. The combined prediction model, with verified accuracy and stability, establishes a theoretical foundation for prediction and maintenance of in-service bridges' structural performance degradation.
-
Key words:
- bridge engineering /
- performance degradation prediction /
- D-S evidence theory /
- Markov chain /
- combination prediction model /
- bridge performance degradation rate
edited-byedited-by1) (我刊编委唐光武来稿) -
表 1 预测模型精度等级
Table 1. Prediction model accuracy levels
accuracy class average relative error Δ posterior difference ratio C class 1 0.01 C≤0.35 class 2 0.05 0.35 < C≤0.50 class 3 0.10 0.50 < C≤0.60 class 4 0.20 C>0.65 表 2 基于ES法预测桥梁技术状况
Table 2. Prediction of bridge technical conditions based on the ES method
age m/a scores Sm(1) Sm(2) Sm(3) am bm cm prediction relative error R/% 1 100 100 100 100 100 0 0 100 0 2 98.1 99.088 0 99.562 2 99.789 9 98.367 2 -0.998 1 -0.105 1 100.00 1.94 3 96.5 97.845 8 98.738 3 99.285 1 96.607 4 -1.609 6 -0.147 3 97.264 0.79 4 95.8 96.863 8 97.838 6 98.590 8 95.666 5 -1.405 4 -0.094 8 94.851 -0.99 5 95.2 96.065 2 96.987 3 97.821 1 95.054 6 -1.052 0 -0.037 6 94.166 -1.09 6 94.3 95.217 9 96.138 0 97.013 2 94.252 9 -0.951 3 -0.019 1 93.965 -0.36 7 93.4 94.345 3 95.277 5 96.180 1 93.383 5 -0.927 8 -0.012 6 93.282 -0.13 8 92.1 93.267 6 94.312 7 95.283 8 92.148 2 -1.133 3 -0.031 6 92.443 0.37 9 90.4 91.891 1 93.150 4 94.259 7 90.482 0 -1.502 9 -0.063 8 90.983 0.65 10 89.3 90.647 4 91.948 9 93.150 5 89.245 9 -1.428 5 -0.042 6 88.915 -0.43 11 88.1 89.424 6 90.737 3 91.992 2 88.054 3 -2.013 7 -0.024 6 87.775 -0.37 12 87.8 88.644 8 89.732 9 90.907 7 87.643 5 -0.807 3 0.037 0 86.016 -2.03 13 86.6 87.663 3 88.739 5 89.867 0 86.638 4 -0.876 9 0.021 9 86.873 0.32 14 85.4 86.576 9 87.701 5 88.827 5 85.453 9 -1.034 6 0.000 7 85.783 0.45 15 84.6 85.628 0 86.706 2 87.809 3 84.574 7 -0.938 7 0.010 6 84.420 -0.21 16 82.8 - - - - - - 83.647 1.02 17 81.1 - - - - - - 82.740 2.02 18 80.2 - - - - - - 81.854 2.06 19 79.1 - - - - - - 80.990 2.39 20 78.0 - - - - - - 80.146 2.75 表 3 基本概率数
Table 3. Basic probabilities
serial number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 relative error R/% 0 1.94 0.79 -0.99 -1.09 -0.36 -0.13 0.37 f(a) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 f(ab) 0 0 0 0 0.18 0 0 0 f(b) 1 0 0 1 0.82 1 1 0.26 f(bc) 0 0 0.42 0 0 0 0 0.74 f(c) 0 1 0.58 0 0 0 0 0 serial number 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 relative error R/% 0.65 -0.43 -0.37 -2.03 0.32 0.45 -0.21 f(a) 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 f(ab) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 f(b) 0 1 1 0 0.36 0.1 1 f(bc) 0.7 0 0 0 0.64 0.9 0 f(c) 0.3 0 0 0 0 0 0 -
[1] 黄侨, 任远, 许翔, 等. 大跨径缆索承重桥梁状态评估的研究现状与发展[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2017, 49(9): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX201709001.htmHUANG Qiao, REN Yuan, XU Xiang, et al. Research progress of condition evaluation for large span cable supported bridges[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017, 49(9): 1-9. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX201709001.htm [2] 占玉林, 斯睿哲, 臧亚美. 混凝土桥梁耐久性2020年度研究进展[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文), 2021, 43(S1): 100-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN2021S1010.htmZHAN Yulin, SI Ruizhe, ZANG Yamei. State-of-the-art review of the durability of concrete bridges in 2020[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 43(S1): 100-106. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN2021S1010.htm [3] 彭容新, 邱文亮, 滕飞. 寒区近海混凝土桥梁性能衰退机理与损伤行为评估方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(12): 129-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202112011.htmPENG Rongxin, QIU Wenliang, TENG Fei. Performance degradation mechanism and damage behavior evaluation method of concrete bridge in cold region marine environment[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(12): 129-146. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202112011.htm [4] 李宏男, 董皓璐, 李超. 基于全寿命周期抗震性能的桥梁结构维修决策方法研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(2): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202002001.htmLI Hongnan, DONG Haolu, LI Chao. Research progress on life-cycle performance-based seismic maintenance decision method for bridge structures[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(2): 1-14. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202002001.htm [5] FRANGOPOL D M, SABATINO D, DONG Y. Bridge life-cycle performance and cost: analysis, prediction, optimization and decision-making[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2017, 13(10): 1239-1257. doi: 10.1080/15732479.2016.1267772 [6] 包龙生, 郝博, 周诗梦, 等. 基于中心点白化权函数的桥梁技术状况评定[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 35(1): 101-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYJZ201901013.htmBAO Longsheng, HAO Bo, ZHOU Shimeng, et al. Bridge technique condition assessment based on central point triangle whiten weight function[J]. Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science), 2019, 35 (1): 101-108. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYJZ201901013.htm [7] 韩晋, 杨岳, 陈峰, 等. 基于非等时距加权灰色模型与神经网络的组合预测算法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2013, 34(4): 408-419. doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2013.04.009HAN Jin, YANG Yue, CHEN Feng, et al. Combination forecasting algorithm based on non-equal interval weighted grey model and neural network[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2013, 34(4): 408-419. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2013.04.009 [8] QIU Y J, AN S K, RAHMAN A, et al. Evaluation and optimization of bridge deck waterproof bonding system using multi-objective grey target decision method[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2020, 21(7): 1844-1858. doi: 10.1080/14680629.2019.1568288 [9] MIAO P, LIU P. Prediction-based maintenance of existing bridges using neural network and sensitivity analysis[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2021, 2021: 4598337. [10] 梁宗保, 胡怡然, 张凯. 桥梁健康监测信息的数据驱动处理方法研究[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2013, 23(10): 258-261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFZ201310067.htmLIANG Zongbao, HU Yiran, ZHANG Kai. Research of data drive processing method of bridge health monitoring information[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2013, 23(10): 258-261. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFZ201310067.htm [11] 夏烨, 王鹏, 孙利民. 基于多源信息的桥梁网级评估方法[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(11): 1574-1584. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ201911006.htmXIA Ye, WANG Peng, SUN Limin. A condition assessment method for bridges at network level based on multi-source information[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2019, 47(11): 1574-1584. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ201911006.htm [12] WU Y, ZHANG L H, LIU H B, et al. Stress prediction of bridges using ANSYS soft and general regression neural network[J]. Structures, 2022, 40(6): 812-823. [13] 张巧灵, 高淑萍, 何迪, 等. 基于时间序列的混合神经网络数据融合算法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(1): 82-91. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.410056ZHANG Qiaoling, GAO Shuping, HE Di, et al. A hybrid neural network data fusion algorithm based on time series[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(1): 82-91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.410056 [14] CHOI Y, LEE J, KONG J. Performance degradation model for concrete deck of bridge using pseudo-LSTM[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(9): 3848. doi: 10.3390/su12093848 [15] TAO W F, LIN P H, WANG N Y. Optimum life-cycle maintenance strategies of deteriorating highway bridges subject to seismic hazard by a hybrid Markov decision process model[J]. Structural Safety, 2021, 89(1): 102042. [16] 代亮, 翟一鸣, 汪贵平. 自供电路侧单元能量-时延均衡分组调度策略[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(2): 161-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC202002013.htmDAI Liang, ZHAI Yiming, WANG Guiping. Packet scheduling scheme for energy-delay tradeoff in self-powered roadside units[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(2): 161-171. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGC202002013.htm [17] 时笑鹏. 中小跨径混凝土梁桥退化预测和维护策略研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2018.SHI Xiaopeng. The degradation prediction and main-tenance strategy of medium & short span concrete girder bridges[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2018. (in Chinese) [18] DIZAJ E A, PADGETT J E, KASHANI M M. A Markov chain-based model for structural vulnerability assessment of corrosion-damaged reinforced concrete bridges[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 2021, 379(2203): 20200290. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2020.0290 [19] FANG Y, SUN L. Developing a semi-Markov process model for bridge deterioration prediction in shanghai[J]. Sustainability, 2019, 11(19): 5524. doi: 10.3390/su11195524 [20] HAN Z Y, ZHAO J, HENRY L, et al. A review of deep learning models for time series prediction[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(6): 7833-7848. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2923982 [21] 张志姝, 高燕. 具有随机扰动和Markov切换的中立型耦合神经网络的自适应同步[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(12): 1381-1391. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.410079ZHANG Zhishu, GAO Yan. Neutral form with random disturbance and Markov switching adaptive synchronization of coupled neural networks[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(12): 1381-1391. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.410079 [22] CHENG X, ZHOU J M, ZHAO X M. Safety assessment of vehicle behaviour based on the improved D-S evidence theory[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(11): 1396-1402. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2019.0737 [23] WANG H, GUO L, DOU Z, et al. A new method of cognitive signal recognition based on hybrid information entropy and DS evidence theory[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2018, 23(4): 677-685. doi: 10.1007/s11036-018-1000-8 [24] 于永堂, 郑建国, 张继文, 等. 基于卡尔曼滤波与指数平滑法融合模型的沉降预测新方法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(S1): 127-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC2021S1025.htmYU Yongtang, ZHENG Jianguo, ZHANG Jiwen, et al. Prediction of settlement based on fusion model of Kalman filter and exponential smoothing algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(S1): 127-131. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC2021S1025.htm [25] 蒋艳辉. 基于指数平滑法与马尔科夫链的道路交通事故预测研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.JIANG Yanhui. Research of road traffic accident prediction based on exponential smoothing and Markov chain[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese) [26] NEGIN A, MAHDI Z, LUDOVIC L. A sequential clustering method for the taxi-dispatching problem considering traffic dynamics[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2020, 12(4): 169-181. doi: 10.1109/MITS.2020.3014444 [27] 李健. 桥梁退化预测模型与最优维护管理决策研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2009.LI Jian. Deterioration prediction model and optimal maintenance strategy for existing bridge[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2009. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载:













 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号