A Fast Re-Modelling Method for Simulation Models by Fusing Geometric Information and Simulation Information
-
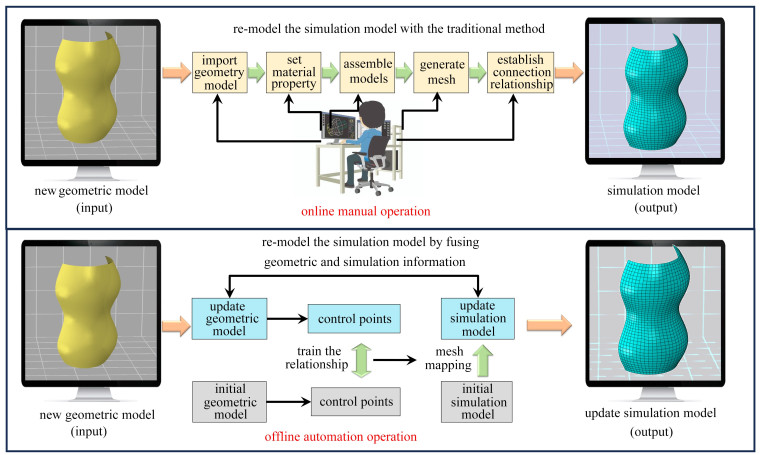
摘要: 复杂结构的设计迭代过程中,往往涉及大量的重建模与重分析,导致计算成本较高且耗时较长. 针对这一挑战,该文提出了一种融合几何与网格信息的仿真模型快速重构方法. 该方法通过精确捕捉复杂几何模型的结构特征并进行数字化表达,进而训练几何模型的特征信息驱动仿真模型进行自动重构. 首先,引入拟共形映射技术对复杂曲面进行平面参数化,通过栅格采样技术获取平面控制点,根据映射前后对应关系生成曲面控制点,作为结构特征的数字化表达;其次,利用径向基函数算法,对修改前后几何模型的控制点进行训练,通过网格映射技术实现对仿真模型的自动化重构. 最后,为了验证所提出方法的有效性,以飞机隔框结构作为典型算例进行研究. 与传统的仿真模型重构方法相比,最大应力误差仅为0.87%. 所需的人机操作步数减少95.40%,模型重构耗时减少96.67%. 结果表明,所提出方法在保证仿真精度的同时,显著降低了仿真模型重构的时间,实现了基于几何与网格模型映射孪生的快速设计.Abstract: In the design iteration process of complex structures, a large amount of re-modelling and re-analysis is often involved, leading to high computational costs and long processing periods. To address this challenge, a fast re-modelling method for simulation models was proposed by fusing geometric and mesh information. The method can accurately capture and digitally represent the structural features of the complex geometric model. Then, the feature information of the geometric model was trained to drive the automatic re-modelling of the simulation model. Firstly, the quasi-conformal mapping technique was introduced to parameterize the complex surfaces. A fixed number of control points were obtained through the voxel sampling, as a digital representation of the structural features. Secondly, the radial basis function algorithm was used to train the control points of the geometric model before and after modification. The automated re-modelling of the simulation model was realized with the mesh-mapping technique. Finally, to verify the effectiveness and practicality of the proposed method, an aircraft frame structure was used as a case study. Compared with the traditional re-modelling method, the proposed method has a simulation analysis error level of stress at only 0.87%. The number of required human-computer interaction steps decreases by 95.40% and the operation time reduces by 96.67%. The results show that, the proposed method significantly reduces the simulation model re-modelling time while ensuring the simulation accuracy, which achieves the rapid design based on the digital twin between geometric and mesh models.
-
表 1 不同模型重构方法对比
Table 1. Comparison of results for different re-modelling methods
maximum displacement/mm maximum stress/MPa consumed time/h steps number of human-computer interaction traditional method 0.11 249.81 1.50 87 proposed method 0.11 247.65 0.05 4 comparison/% 0.00 -0.87 -96.67 -95.40 -
[1] 胡嘉欣, 芮姝, 高瑞朝, 等. 飞行器结构布局与尺寸混合优化方法[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43 (5): 225363.HU Jiaxin, RUI Shu, GAO Ruichao, et al. Hybrid optimization method for structural layout and size of flight vehicles[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43 (5): 225363. (in Chinese) [2] KHAN H A, SHAHID A, KHUSHBASH S, et al. Investigation of failure and development of mitigation techniques of a cracked aircraft wing spar cap[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2023, 147: 107149. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107149 [3] 张永杰, 周静飘, 石磊, 等. 基于PRSEUS结构的翼身融合民机中央机体球亏面框优化设计方法[J]. 航空学报, 2024, 45 (12): 229331.ZHANG Yongjie, ZHOU Jingpiao, SHI Lei, et al. Optimization design method of central fuselage spherical deficient surface frames in blended-wing-body civil aircraft based on PRSEUS structure[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2024, 45 (12): 229331. (in Chinese) [4] 张伦武, 周堃, 赵方超, 等. 装备环境适应性研究进展及展望[J]. 装备环境工程, 2024, 21 (5): 1-12.ZHANG Lunwu, ZHOU Kun, ZHAO Fangchao, et al. Research progress and prospect of materiel environmental worthiness[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2024, 21 (5): 1-12. (in Chinese) [5] 吴建国, 李海波, 冯国林, 等. 新形势下航天装备环境试验技术的未来发展趋势[J]. 装备环境工程, 2024, 21 (5): 34-40.WU Jianguo, LI Haibo, FENG Guolin, et al. Future development trend of environmental testing technology for aerospace equipment under new circumstances[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2024, 21 (5): 34-40. (in Chinese) [6] BAZILEVS Y, CALO V M, COTTRELL J A, et al. Isogeometric analysis using T-splines[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 199 (5/6/7/8): 229-263. [7] SUN Y, ZHOU Z, LAI P, et al. Isogeometric analysis-based buckling optimization framework for grid-stiffened shells using asymptotic homogenization method and Rayleigh-Ritz method[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2022, 65 (11): 330. doi: 10.1007/s00158-022-03441-4 [8] NINIĆ J, BUI H G, MESCHKE G. BIM-to-IGA: a fully automatic design-through-analysis workflow for segmented tunnel linings[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2020, 46: 101137. doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2020.101137 [9] HAO P, WANG Y, JIN L Z, et al. An isogeometric design-analysis-optimization workflow of stiffened thin-walled structures via multilevel NURBS-based free-form deformations (MNFFD)[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 408: 115936. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2023.115936 [10] 金灵智, 王禹, 郝鹏, 等. 加筋路径驱动的板壳自适应等几何屈曲分析[J]. 力学学报, 2023, 55 (5): 1151-1164.JIN Lingzhi, WANG Yu, HAO Peng, et al. Adaptive isogeometric buckling analysis of stiffened panels driven by stiffener paths[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2023, 55 (5): 1151-1164. (in Chinese) [11] HAO P, LIU D C, LIU H, et al. Intelligent optimum design of large-scale gradual-stiffness stiffened panels via multi-level dimension reduction[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2024, 421: 116759. [12] WOBBES E, BAZILEVS Y, KURAISHI T, et al. Complex-geometry IGA mesh generation: application to structural vibrations[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2024, 74 (2): 247-261. [13] RANK E, RUESS M, KOLLMANNSBERGER S, et al. Geometric modeling, isogeometric analysis and the finite cell method[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 249: 104-115. [14] PERDUTA A, PUTANOWICZ R. Tools and techniques for building models for isogeometric analysis[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2019, 127: 70-81. [15] CAMBA J D, CONTERO M, COMPANY P, et al. The cost of change in parametric modeling: a roadmap[J]. Computer-Aided Design and Applications, 2020, 18 (3): 634-643. [16] IYER N, JAYANTI S, LOU K, et al. Three-dimensional shape searching: state-of-the-art review and future trends[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2005, 37 (5): 509-530. [17] MOHR J, KLEINSCHRODT C, TREMMEL S, et al. Compatibility improvement of interrelated items in exchange files: a general method for supporting the data integrity of digital twins[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12 (16): 8099. [18] VASANTHA G, PURVES D, QUIGLEY J, et al. Common design structures and substitutable feature discovery in CAD databases[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2021, 48: 101261. [19] YUN H, KIM E, KIM D M, et al. Machine learning for object recognition in manufacturing applications[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2023, 24 (4): 683-712. [20] WU H, LEI R, PENG Y, et al. AAGNet: a graph neural network towards multi-task machining feature recognition[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2024, 86: 102661. [21] NING F, SHI Y, CAI M, et al. Part machining feature recognition based on a deep learning method[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2023, 34 (2): 809-821. [22] ZUBAIR A F, ABU MANSOR M S. Automatic feature recognition of regular features for symmetrical and non-symmetrical cylinder part using volume decomposition method[J]. Engineering With Computers, 2018, 34: 843-863. [23] HOU B, HUANG Z, ZHOU H, et al. A hybrid hint-based and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method for optimal parting curve generation in injection mold design[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 112: 2133-2148. [24] YAO X, WANG D, YU T, et al. A machining feature recognition approach based on hierarchical neural network for multi-feature point cloud models[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2023, 34 (6): 2599-2610. [25] XIAO A, HUANG J, GUAN D, et al. Unsupervised point cloud representation learning with deep neural networks: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45 (9): 11321-11339. [26] COLLIGAN A R, ROBINSON T T, NOLAN D C, et al. Point cloud dataset creation for machine learning on CAD models[J]. Computer-Aided Design and Applications, 2021, 18 (4): 760-771. [27] WANG Y, SUN Y, LIU Z, et al. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38 (5): 1-12. [28] YEO C, KIM B C, CHEON S, et al. Machining feature recognition based on deep neural networks to support tight integration with 3D CAD systems[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11 (1): 22147. [29] TIAN K, LI H Q, HUANG L, et al. Data-driven modelling and optimization of stiffeners on undevelopable curved surfaces[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2020, 62: 3249-3269. [30] LI H Q, LI Z C, CHENG Z Z, et al. A data-driven modelling and optimization framework for variable-thickness integrally stiffened shells[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2022, 129: 107839. [31] LI H Q, LIU X W, GAO Y M, et al. Active learning-driven control point optimization method for efficient modeling of complex stiffened curved shells[J]. Engineering Structures, 2024, 302: 117412. [32] VOGIATZIS P, MA M, CHEN S, et al. Computational design and additive manufacturing of periodic conformal metasurfaces by synthesizing topology optimization with conformal mapping[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 328: 477-497. [33] NIAN X, CHEN F. Planar domain parameterization for isogeometric analysis based on Teichmüller mapping[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 311: 41-55. [34] 付君健, 徐勇, 周祥曼, 等. 基于联合仿真的曲面共形多孔结构拓扑优化方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50 (9): 2781-2790.FU Junjian, XU Yong, ZHOU Xiangman, et al. Topological optimization method for conformal cellular structures on surfaces based on co-simulation[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50 (9): 2781-2790. (in Chinese) [35] MENG T W, CHOI G P T, LUI L M. TEMPO: feature-endowed Teichmüller extremal mappings of point clouds[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2016, 9 (4): 1922-1962. [36] QUINN J A, LANGBEIN F C, LAI Y K, et al. Generalized anisotropic stratified surface sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2013, 19 (7): 1143-1157. -





 下载:
下载:










 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号